Secondary Antibody Resource

Multiple Labeling Protocol Generator
This tool may help in the design your experiment. It will apply the criteria outlined above to identify the potential cross-reactivity between primary antibodies and therefore the minimal cross-reactivity each secondary antibody will require.

FENS 2022
JIR was delighted to return to the very much-awaited FENS Neuroscience conference. Hosted in Paris, FENS 2022 was the perfect opportunity to unveil our latest product, AffiniPure-VHH™ Secondary Antibodies. Read more to find out about the winners of our Chocolate brain prize draw and how you can acquire a JIR T-Shirt!

Case Study: Diagnostic Applications: Allergy
Allergy affects many people and has multiple causes including pet dander, pollen, and chemical allergens. It may manifest as skin irritations or rhinitis, through to the more serious such as allergic asthma and life-threatening anaphylaxis. Allergy is commonly diagnosed using immunoassays which can identify the causative agent and the disease’s severity. In this article, we introduce allergy and present two immunotechniques commonly used to characterize and diagnose allergies.
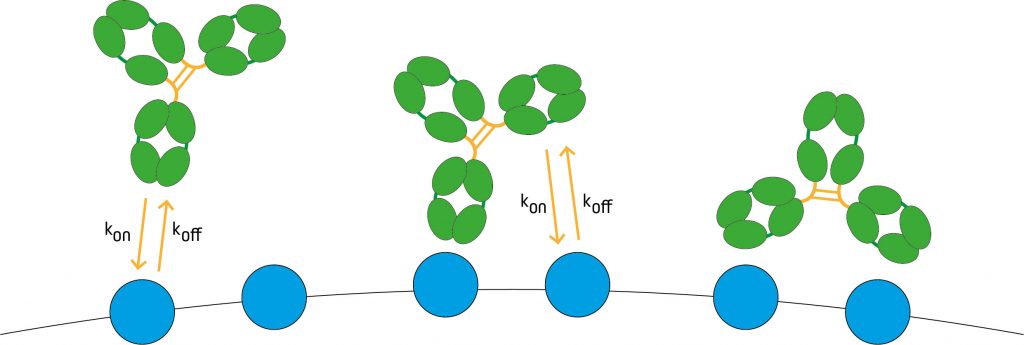
Affinity vs Avidity
Antibody basics
Antibodies are expressed on the surface of B cells, one of the major cell types involved in adaptive immunity. Because each B cell must express a unique antibody for an individual to mount an effective immune response, an almost infinite number of antibodies exists. Antibody diversity is achieved via three main mechanisms – V(D)J recombination, junctional diversification, and somatic hypermutation – with the latter producing higher affinity antibodies (affinity maturation) as the adaptive immune response unfolds. Affinity is one of two key properties that defines the overall strength of the antibody-antigen interaction. The other is avidity, which has a different meaning.

Troubleshooting using anti-light chain antibodies
Anti-light chain antibodies are commonly used for Western blotting (WB) after Immunoprecipitation (IP) when detecting proteins that migrate to approximately 50kDa with IP and WB primary antibodies from the same host species. These proteins would otherwise be obscured by detection of the heavy chain from the precipitating antibody. Unlike whole molecule-specific antibodies, which detect both heavy and light chains, the anti-IgG, Light Chain Specific antibodies only detect light chains. Consequently, the native primary antibodies used for WB are detected by recognition of their light chains, while the heavy chain of the IP antibody is not detected. Consequently, proteins of interest of approximately 50 kDa can be resolved on a blot without an overlapping signal from the IP antibody heavy chain.

